Problem
Part of VMware infrastructure maintenance involves upgrading vmtools. Although many ways exist, most out-of-the-box tasks do not cover real-world scenarios, so some functions must be performed manually or semi-manually. Today, we will explore how to address these gaps and automate the vmtools upgrade as much as possible using intelligent methods.
We are going to support the following scenarios:
- VM templates
- Powered off VM
- Suspended VMs
- Linux/Windows
- VMware/3rd party vmtools
- Depended/Independent disks
- Automatically created/deleted snapshots before/after the upgrade
To the VSCode!
Solution
The workflow logic is described in the diagram below.
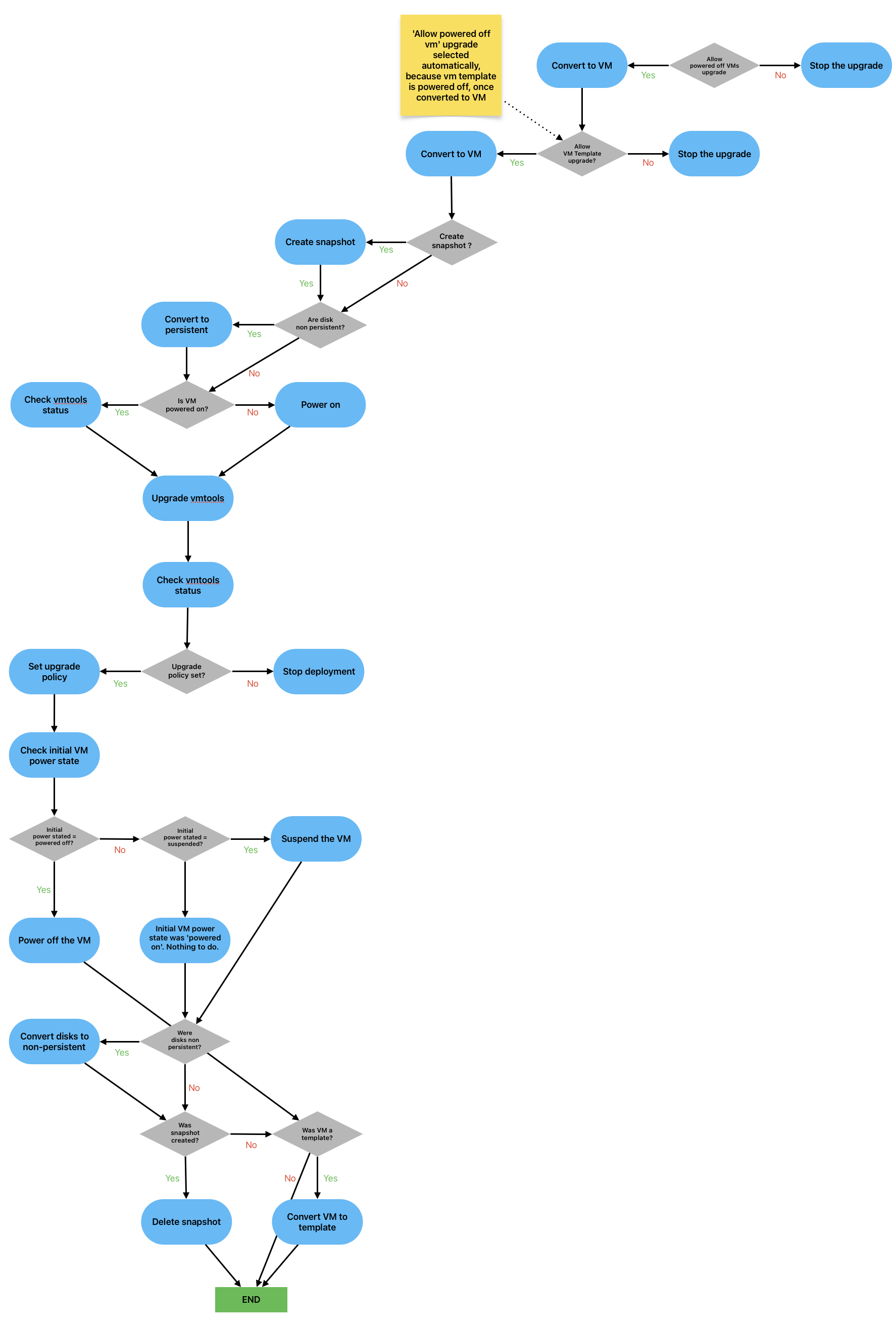
The original size PDF of the diagram can be found here.
As usual, the main logic is written in the workflow, and all the functions are in the separate Functions class.
Custom form
Our dynamic custom form allows us to show or hide inputs based on the user’s scenario. Some inputs have default values that can be overwritten. I selected all of them to display on the screen. 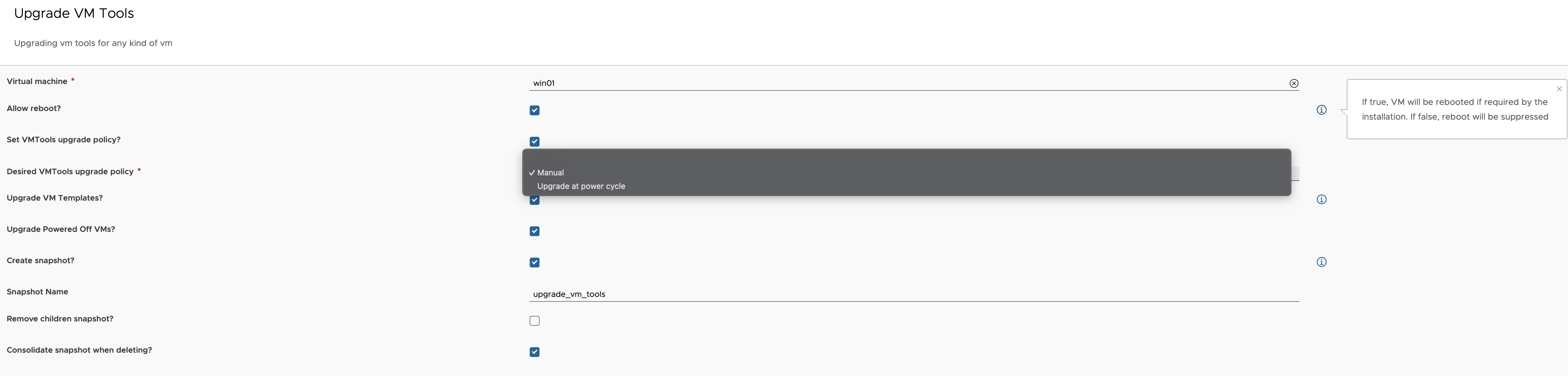
Main workflow
First of all, we have a few static variables.
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 |
const func = new Functions(); const shutdownTimeout = 10; // seconds const vmtoolsTimeout = 10; // minutes const waitForTools = true; const snapshotDescription = `Upgrade VM Tools. Created by ${Server.getCurrentLdapUser()}`; const snapshotWithMemory = false; const snapshotWithQuiesce = false; enum diskPersistencyType { persistent = "persistent", nonpersistent = "independent_nonpersistent", } |
Some of this variables, like
shutdownTimeoutorvmtoolsTimeoutcan be converted to inputs if we want to provide more granular control to the user.
Let’s verify whether the VM is configured as a template, then ascertain its current power state. Our subsequent actions will be determined by the existing status and the inputs provided in the workflow.
1 2 3 4 5 6 |
const isVmTemplate = func.isVmTemplate(vm); const initialPowerState = func.getVmPowerState(vm); if (!allowUpgradePoweredOffVms && initialPowerState === "poweredOff") throw new Error("VM is powered off and not allowed for upgrade"); if (!allowUpgradeTemplates && isVmTemplate) throw new Error("VM is template and templates are not allowed for upgrade"); |
If no error was thrown, let’s check if the VM is a template. If so, we need to convert it to a regular VM.
- How to build a website with WordPress and what are the best plugins to use Building a website with WordPress is an excellent choice due to its versatility, ease of use, and a vast array of plugins that enhance functionality. Here’s a comprehensive guide to building a WordPress website, along with recommendations for the best plugins
- Top WordPress Plugins for Managing Ads and Monetizing Your Website Effectively: Why is Ads Management Important for Website Monetization? Strategic ad placement throughout the website enables publishers to maximize ad revenue while ensuring a positive user experience. The positioning of ads is critical in capturing users’ attention without being intrusive or disruptive. By understanding user behavior and preferences, publishers can make informed decisions regarding ad placement to ensure that the ads are relevant and engaging.
- Top Directory Plugins for WordPress to Create Professional Listings and Directories: If you are interested in establishing professional listings and directories on your WordPress website, the following information will be of value to you. This article will present the top directory plugins available for WordPress, which include GeoDirectory, Business Directory Plugin, Sabai Directory, Connections Business Directory, and Advanced Classifieds & Directory Pro.
- The Most Important Stages and Plugins for WordPress Website Development: Developing a WordPress website requires careful planning, execution, and optimisation to ensure it is functional, user-friendly, and effective. The process can be broken into key stages, and each stage benefits from specific plugins to enhance functionality and performance. Here’s a detailed guide to the most important stages of WordPress website development and the essential plugins for each stage.
- .org vs .com: A Top Guide to the Differences in Domain Extension
When you set up a website for a business or a non-profit organisation, you might think the most important part of the address is the actual name. But the domain extension (the bit that comes after the dot) is just as important for telling people what your site is all about. - The Best WordPress Plugins for Image Optimization to Improve Load Times and SEO. The pivotal element lies in image optimization. This discourse delves into the significance of image optimization for websites and its impact on load times. Furthermore, we will delve into the advantages of leveraging WordPress plugins for image optimization, such as streamlined optimization processes, enhanced SEO, expedited load times, and an enriched user experience.
- What is a data center or Internet data center? The term “data center” has become very common due to the role it plays in many of our daily activities. Most of the data we receive and send through our mobile phones, tablets and computers ends up stored in these data centers — which many people refer to as “the Cloud”, in a more generic way.
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 |
if (isVmTemplate) { const currentHostSystem = func.getVmParentHost(vm); const currentComputeResource = func.getComputeResource(currentHostSystem); //@ts-ignore const currentResourcePool = func.getResourcePool(currentComputeResource); const vars = { vm: vm, pool: currentResourcePool, host: currentHostSystem, }; func.convertTemplateToVm(vars); } |
The next step is to check if the user requested to create a snapshot. It is not possible to take a snapshot of a template. The snapshot will be made with a default name, “upgrade_vm_tools” (which can be changed). When the snapshot is deleted, the removeSnapshot function will only seek the snapshot with that name. This is essential because the VM may have multiple snapshots, and we don’t want to delete the others.
1 |
if (createSnapshot) func.createVmSnapshot(vars); |
The createVmSnapshot function itself is pretty straightforward
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 |
public createVmSnapshot({ vm, name, description, memory, quiesce }: { vm: VcVirtualMachine; name: string; description: string; memory: boolean; quiesce: boolean }) { if (!vm.name || !name || !description) { throw new Error("Required parameters are missing"); } try { const task: VcTask = vm.createSnapshot_Task(name, description, memory, quiesce); System.getModule("com.vmware.library.vc.basic").vim3WaitTaskEnd(task, true, 2); System.log(`Creating snapshot '${name}' on VM '${vm.name} was completed successfully'`); } catch (error) { throw new Error(`Failed to create snapshot '${name}' on VM '${vm.name}': ${error}`); } } |
As a result, we have a snapshot with an informative description. 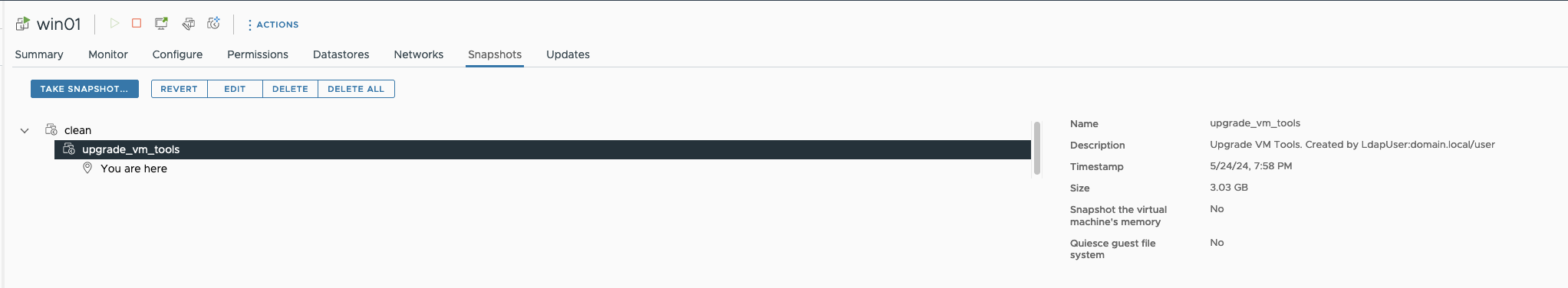
It is important not to change the snapshot’s name, because the workflow will search for a snapshot with the name it was created with.
Now, we will check the type of the disks – if they exist first of all, and if so, if they are persistent. If not, we temporarily convert them to persistent.
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 |
const vmDisks = func.getVmDisks(vm); if (!vmDisks) throw new Error(`No disks found for virtual machine '${vm.name}'`); const isDiskNonPersistent = func.getVmNonPersistentDisks(vmDisks, diskPersistencyType.persistent).length !== 0; if (isDiskNonPersistent) { System.log(`Preparing disks for conversion to ${diskPersistencyType.persistent}`); func.shutdownVmBasedOnCurrentState(vm, shutdownTimeout); if (vm.snapshot != null) throw new Error("Disks cannot be converted because the virtual machine has at least one snapshot"); const diskPersistency: VcVirtualMachineConfigSpec = func.prepareVmDiskPersistency(vmDisks, diskPersistencyType.persistent); func.changeVmDiskPersistency(diskPersistency, vm); } |
Its a time to upgrade the vmtools.
1 2 3 4 |
if (initialPowerState !== "poweredOn") func.powerOnVm(vm); func.checkVmToolsStatus(vm, vmtoolsTimeout); func.upgradeVmTools({ vm, allowReboot, waitForTools }); func.checkVmToolsStatus(vm, vmtoolsTimeout); |
The upgradeVmTools function can check all available statuses of the vmtools and proceed accordingly.
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 |
switch (toolsStatus) { case "guestToolsSupportedNew": System.log("VMtools are newer than available. Skipping the upgrade"); case "guestToolsUnmanaged": System.log("3rd party managed VMtools (open-vm-tools). Skipping the upgrade"); case "guestToolsCurrent": System.log("VMware Tools are already running and up to date. Nothing to do."); return true; case "guestToolsBlacklisted": case "guestToolsNeedUpgrade": case "guestToolsSupportedOld": System.log("Starting VMware Tools upgrade..."); const upgradeArgs = allowReboot ? "/s /vqn" : '/s /v"/qn REBOOT=ReallySuppress"'; try { const task = vm.upgradeTools_Task(upgradeArgs); System.getModule("com.vmware.library.vc.basic").vim3WaitTaskEnd(task, true, 2); System.log("VMware Tools have been upgraded."); ... |
In the function above, we also support silent upgrades (without reboot) if requested in the custom form.
1 |
const upgradeArgs = allowReboot ? "/s /vqn" : '/s /v"/qn REBOOT=ReallySuppress"'; |
The next step is to configure the vmtools upgrade policy if selected.
1 |
if (setVmToolsUpgradePolicy) func.setVmToolsUpgradePolicy(vm, desiredVmToolsUpgradePolicy); |
Once the upgrade is done, we should return the VM to its original state: power and persistence.
1 2 3 4 5 6 |
if (initialPowerState === "poweredOff") func.handlePoweredOnVm(vm, shutdownTimeout); if (initialPowerState === "suspended") func.handleSuspendedVm(vm); if (isDiskNonPersistent) { const diskPersistency: VcVirtualMachineConfigSpec = func.prepareVmDiskPersistency(vmDisks, diskPersistencyType.nonpersistent); func.changeVmDiskPersistency(diskPersistency, vm); } |
In both cases (powered on and suspended), we always strive to act gracefully if possible and decisively if not. An example below.
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 |
public handlePoweredOnVm(vm: VcVirtualMachine, shutdownTimeout: number): void { System.getModule("com.vmware.library.vc.vm.tools").vim3WaitToolsStarted(vm, 2, 5); const vmToolsRunning = vm.vmToolsStatus === "guestToolsRunning"; try { if (vmToolsRunning) { this.shutdownVmGracefully(vm, shutdownTimeout); } else { this.powerOffVmUngracefully(vm); } } catch (e) { System.log(`Failed to wait for vmtools: ${e}. Will try to force shutdown`); try { this.powerOffVmUngracefully(vm); } catch (e) { throw new Error(`Failed to power off VM '${vm.name}': ${e}`); } System.log(`VM '${vm.name}' powered off successfully`); } } |
The last step would be to remove the snapshot if it was created and convert the VM to the template if it was a template.
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 |
if (createSnapshot) { const snapshotVars = { vm: vm, removeChildren: removeChildren, consolidate: consolidate, snapshotName: snapshotName }; func.removeSnapshot(snapshotVars); } if (isVmTemplate) func.convertVmToTemplate(vm); |
Summary
In the article, we covered the wide-ranging use case of upgrading vmtools. We aimed to automate this process as much as possible and save time. We also developed user-friendly custom forms with various options for users to choose from.
Next step
In the next part, we’ll add more functionality and allow the VM Hardware upgrade as well.
Source Code
The source code with the unit tests can be found here